- HOME
- Environment(E)
- Water Resources / Water Environment
For Resolving individual issues of The Water Resources and the Water Environment
Policies and Basic Approach
The TAISEI Group has formulated "TAISEI Green Target 2050" as the Group's long-term environmental target to realize the "Sustainable and Environmentally Friendly Society" promoted in its environmental policy. The TAISEI Green Target 2050 establishes the responsibilities relating to individual issues conserving water resources and water environment, as well as the business activities that are conducted and their contribution to the achievement of these targets. The basic approach is outlined in the environmental policy.
Responsibilities
As construction is the core business of the Taisei Group, the Group has a keen awareness of the effect of its business activities on water resources and water environment and the impact of water resources and water environment on business activities. We consider it to be our responsibility to exercise appropriate management and reduce water use, and to minimize the adverse impact of construction business on water resources and water environments.
Contribution Through Our Business Activities
The Taisei Group identifies risks and opportunities related to with water resources and water environments. We strive to develop and disseminate technologies and services relating to conservation and restoration, and to promote business activities that are in harmony with nature in order to maximize the positive impact and contribute to sustainable water resources and water environments.
Policies / Commitments
- Action Guidelines for Taisei: Promoting environmental conservation and creation
- Environmental Policy
- TAISEI Green Target 2050: The Two Individual Issues
- Promise of Eco-First
- Taisei Group Sustainable Procurement Guidelines
- Green Procurement Standard Guideline
Goals
Group’s Long-Term Environmental Targets (TAISEI Green Target 2050)
We have established the Group's long-term environmental targets for 2050, the TAISEI Green Target 2050, and have been working to achieve three types of societies (Decarbonized Society, Recycling-Oriented Society, and Nature Co-Existing Society) as well as to resolve two individual issues (Forest Resources / Forest Environment and Water Resources / Water Environment).
Target for addressing two individual issues
| Forest Resources & Forest Environment | Water Resources & Water Environment |
|---|---|
|
|
Activities / Efforts
TAISEI Corporation not only constructs water infrastructure facilities, but also develops and disseminates technologies and services to conserve and revitalize water resources, to promote business activities that are in harmony with nature in order to contribute to achieve sustainable water resources and water environment.
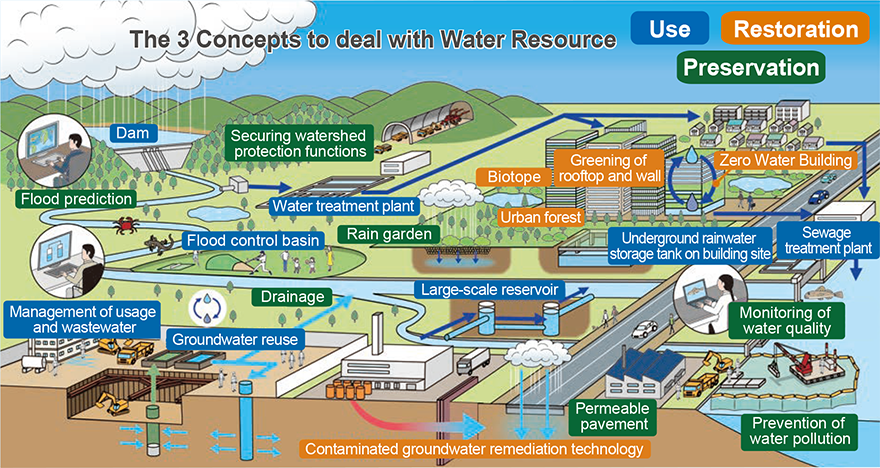
| Sustainable water use | Restoration of water resources | Conservation of water resources |
|---|---|---|
Effective use and reduction of water use (the Water 3Rs)
|
Development and dissemination of technologies and services
|
Reduction of water environment burden
|
Ⅰ. Sustainable Water Use
Effective Use of Water Resources
Taisei Corporation is promoting the TSA:TAISEI Sustainable Action®, a series of activities involving all employees with the aim of reducing environmental load.

In 2011, Taisei began its "CO2 Zero Action" initiative at all construction worksites. This initiative consists of seven basic activities aimed at reducing environmental load. One of the activities was "the effective use of rainwater and spring water," and this activity continues to this day.
In 2018, a "TSA Action List" was prepared, listing specific activities to reduce environmental load. One item included on the list was "Cyclic use and reuse of construction water (including on-site use of rainwater and spring water)." Taisei works to enable reuse of the water from construction operations by purifying it according to the intended purpose of use, and to use rainwater and spring water within the construction site for sprinkling and cleaning the tires of construction vehicles and so on. The TSA Action List is reviewed each year and updated to add new measures, etc.
In particular, work related to slurry shield tunnel construction and to soil contamination countermeasures involves enormous quantities of water. To reduce the quantity of water used, muddy water (sediment transport water and water used for cleaning) is subjected to turbid water treatment, and the resulting recycled water is used.
Taisei also promotes the use of low-flush toilets and water-saving faucets at its head and branch offices and all approximately 600 of its site workplace offices, and is making company-wide efforts to reduce water use.
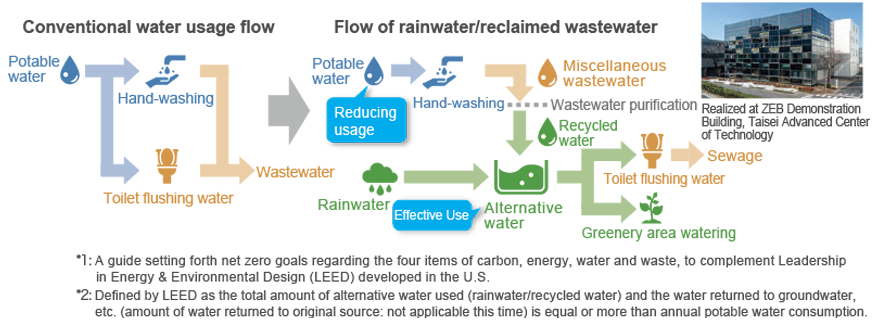
Furthermore, the Taisei Advanced Center of Technology "ZEB Demonstration Building" (Human Space Lab) collects rainwater that falls on the solar panels mounted on its roof in a rainwater use tank. This water is used to flush toilets on the first and second floors.
For its supply chain, Taisei established the "Taisei Group Sustainable Procurement Guidelines", a guideline that indicate code of conduct in areas such as the environmental protection, human rights and compliance that must be observed throughout the supply chain. They summarize matters to be implemented through cooperation between our Group and business partners; all subcontractors and suppliers are required to comply with these guidelines. Taisei also works with all its suppliers to preserve water resources by reducing water use as well as ensuring efficient use, reduction, and adequate management of industrial waste, hazardous chemical substances, and contaminants in addition to compliance with environment-related laws and regulations so as to prevent environmental accidents.
Furthermore, as a collaborative environmental effort with industry organizations and government agencies, Taisei participates in the public-private Water Project* led by the Ministry of the Environment, which promotes initiatives for maintaining and restoring healthy water environments. Taisei shares information on its activities with other companies while promoting initiatives related to water conservation and water risks, such as reducing water use.
In addition, Taisei endorses the mission of the Japan Water Forum (JWF), an NPO working to resolve water issues in collaboration with U.N. agencies and other international organizations as well as local NGOs.

- *The Water Project is a project founded in 2014 by the Ministry of the Environment, based on the Basic Act for Water Circulation, with the aim of creating a venue for public-private cooperation.
Taisei Corporation's total water intake and discharge
Unit: 1000 m3
| FY 2018 | FY 2019 | FY 2020 | FY 2021 | FY 2022 | FY 2023 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intake | 1,436 | 1,414 | 1,412 | 2,266 | 2,279 | 2,012 |
| Discharge | 4,483 | 4,288 | 6,625 | 9,677 | 3,014 | 3,948 |
- Note:As construction locations change each year, comparisons with the previous year would not be useful.
Energy Generating Groundwater Treatment Technology Decarbonization
A Membrane Bio Reactor (MBR) *1, a new sewage treatment technology combining anaerobic treatment*2 and membrane separation technology*3, has been developed, and the performance of the technology is currently being confirmed using test equipment installed at a sewage treatment plant. Compared to the conventional activated sludge method, this technology not only uses less energy but also can collect methane which can be used for power generation, so it is expected to contribute to energy consumption reduction and energy creation*4 in sewage treatment system.
- *1Anaerobic MBR
A process that combines anaerobic treatment and membrane separation technology. Use of a separation membrane makes it possible to maintain a high concentration of the microorganisms needed for decomposition and improve the water quality of the treated water. - *2Anaerobic treatment
Method of converting into biomass (composed of methane and carbon dioxide) the organic matter included in organic wastewater, wastes, etc., using the metabolic action of multiple strains of anaerobic bacteria under anaerobic conditions with no oxygen. - *3Membrane separation technology
Method in which membranes are used to separate water and solids. - *4Energy creation
Biogas generated through anaerobic MBR processing is converted into electricity and heat through gas engines.
Business Activities in Water-stressed Regions
As stated in the TAISEI Green Target 2050, the Group's long-term environmental targets for 2050, we are committed to minimizing adverse impact on water resources and the environment through appropriate management and reduction of water use as part of our efforts toward resolving issues with water resources and water environments. In particular, we implement stricter water management in regions with high water stress.
All worksite the Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas*1 of the World Resource Institute is used to determine the water risk in each region where business activities (civil engineering and construction) are conducted, and appropriate measures are taken for business activities in high water stress regions.
(1) Business activities in Japan
A check using the Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas of the locations where approximately 650 workplaces and head and branch offices in Japan are located revealed that there were no workplaces or offices in regions with a water stress*2 assessment of (4) High or greater.
(2) Business activities overseas
A check using the Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas of the locations of the main overseas workplaces revealed that there were 12 workplaces locating in a water stress*2 assessment of "High" or "Extremely high" region. Appropriate management is being conducted for all workplaces including these 12 workplaces.
- *1Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas: A water risk analysis tool that assesses water risk in five levels using 13 indicators in three categories (water quantity, water quality, and regulatory and reputational risk).
- *2Water stress: An indicator of the degree to which water resources are under stress, derived by dividing annual water intake by annual water runoff.
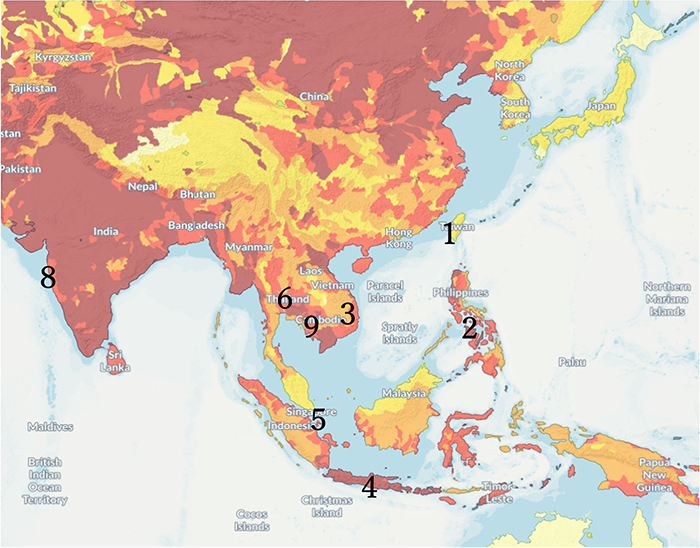
Asia region
Africa region
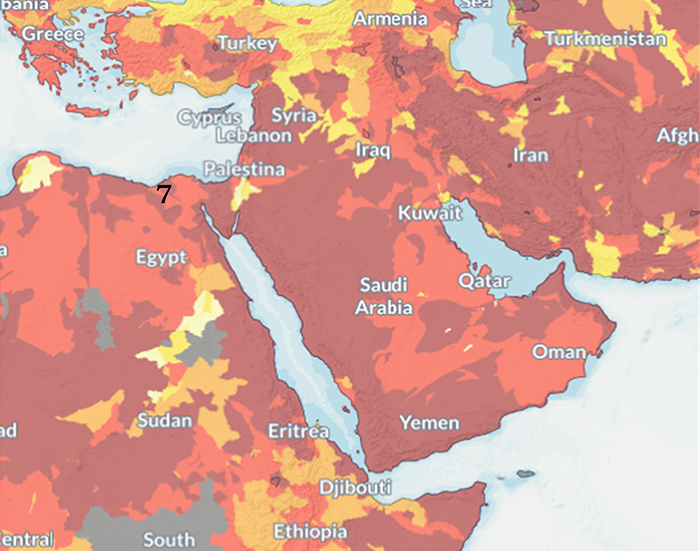
Source:https://www.wri.org/aqueduct
Map numbers indicate country numbers in the table at right.
| No. | Country / region | No. of workplaces | Water risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Taiwan Taipei, Taichung, etc. | 4 | ②Low -medium |
| 2 | Philippines Manila, etc. | 3 | ④High |
| 3 | Vietnam Hanoi, etc. | 2 | ④High |
| Vietnam Ho Chi Minh City, etc. | 1 | ④High | |
| 4 | Indonesia Jakarta | 2 | ⑤Extremely high |
| Indonesia West Java Province | 2 | ⑤Extremely high | |
| 5 | Singapore | 2 | ①Low |
| 6 | Thailand Rayong Province, etc. | 6 | ③Medium - high |
| 7 | Egypt Alexandria | 1 | ⑤Extremely high |
| 8 | India Mumbai | 1 | ④High |
| 9 | Cambodia Phnom Penh Capital City | 1 | ③Medium -high |
| Water risk in locations with workplaces | No. of workplaces | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| ⑤Extremely high | 5 | 20% |
| ④High | 7 | 28% |
| ③Medium - high | 7 | 28% |
| ②Low - medium | 4 | 16% |
| ①Low | 2 | 8% |
Ⅱ. Restoration of Water Resources
Water Environment Technology to Realize Zero Water Buildings (ZWBs)
At the “Human Space Lab (ZEB Demonstration Building)” of the Taisei Advanced Center of Technology, we conducted technology demonstrations to achieve LEED Zero Water*2 as defined in the LEED ZERO Program Guide*1 and obtained the first “LEED Zero Water” certification in Japan in 2024.
We expanded the use of reclaimed water by using reclaimed water purified from rainwater and wastewater from hand washing and other processes in the building for toilet flushing and other purposes. As a result of the year-long technology demonstration, the total annual use of rainwater and reclaimed water (alternative water) exceeded that of tap water.
3rd rain reservoir project of the Shibaura Water Reclamation Center

This facility collects sewage from all parts of Minato Ward, most parts of Chiyoda, Chuo, Shinjuku and Shibuya Wards and some parts of Bunkyo, Toyoshima, Shinagawa, Meguro and Setagaya Wards and then treats it and discharges it into Tokyo Bay. The project was to construct a a rain reservoir to serve as a combined sewerage system improvement facility to store the initial rainwater that is collected and improve the water quality at the discharge location.
Shinagawa Season Terrace
Joint project with co-developer Tokyo Metropolitan Government Bureau of Sewerage

(Photo: Forward Stoke inc.)
An environmentally friendly office building was built on the grounds of the Shibaura Water Reclamation Center owned by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Bureau of Sewerage. The building used a previously unprecedented development method in which a sewerage facility was placed underground and a business and commercial building was constructed above. This was a public-private partnership project by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government and NTT Urban Development Corporation, Taisei Corporation, Mizuho Trust & Banking Co., Ltd. and Tokyo City Development Co., Ltd.
The facility will provide water for a variety of uses, including treated water produced by purifying kitchen wastewater, reclaimed water from purification and treatment of restroom sink wastewater and so on, reclaimed water purchased and brought infrom the Sewage Bureau, and rainwater for toilet flushing water and plant watering, etc.
Ochanomizu Sola City

This development project is being promoted by a Special Purpose Corporation with investment by three companies: Taisei Corporation, Yasuda Real Estate Co., Ltd. and Taisei-Yuraku Real Estate Co.
This facility will receive the spring water and the rainwater that falls on the site and roof of Shin-Ochanomizu Station on the Chiyoda Subway Line, after which the water will be filtered and used as cooling water for the water-cooled chillers, as well as for the automatic sprinklers that water the outdoor plants and as toilet flush water, in order to ensure effective water use.
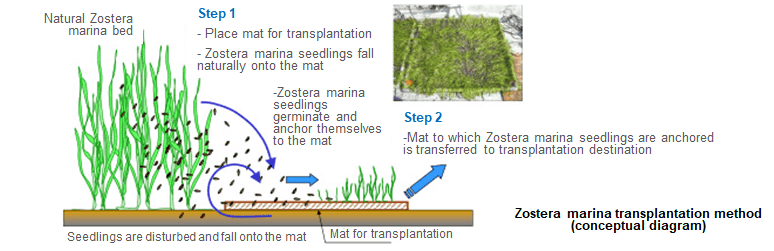
Eelgrass Transplantation Technique
This is a simple transplantation technique for eelgrass (Zostera marina) that requires no seeding or stock planting. A mat made of palm fibers is placed in a natural eelgrass bed, and eelgrass seedlings fall naturally onto the mat and sprout, anchoring themselves to the mat. The mat is then simply moved to the transplantation location. In ocean tests, this method has been confirmed to achieve propagation and growth that is equivalent to that of natural eelgrass.
Coral Transplantation Technology
This technology uses coral egg-laying to induce propagation. Incubated and hatched coral larvae are colonized to implantation devices to propagate. TAISEI has developed a concrete implantation device that is cheaper than conventional ceramic implantation devices. These devices can be used to preserve and create highly diverse coral reefs in the same manner as natural coral reefs are created.

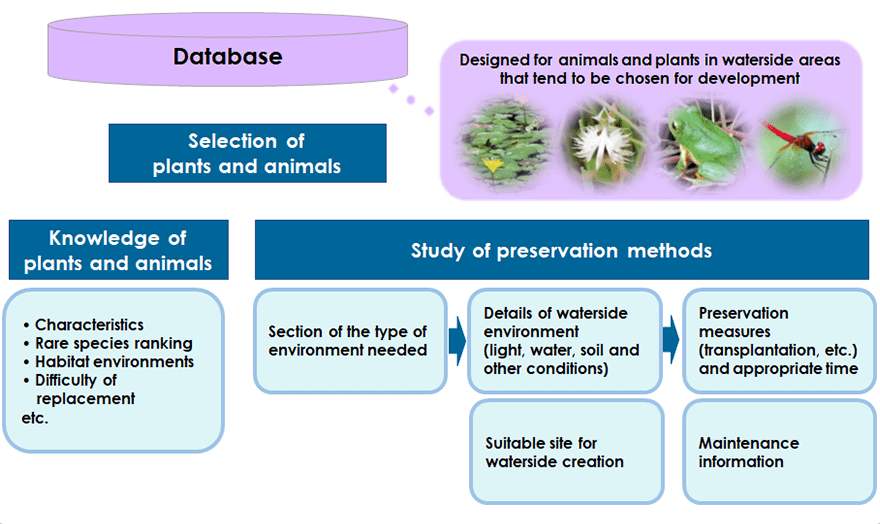
Mizube Concierge
This tool makes it possible to study and plan preservation sites for rare animals and plants quickly, for example to create replacement sites to protect rare animals and plants that inhabit waterside areas near construction sites. A tablet shows the information needed to formulate preservation sites visually in an easily understandable way, making it easy to share information and smoothly achieve consensus with related entities, as well as quickly preparing preservation plans (selecting appropriate replacement candidate sites and so on).
- Entering the name of a rare animal or plant displays the information needed to formulate preservation plans in an easily understandable visual manner.
- Candidate sites where waterside environments can be created as replacement sites can be appropriately selected.
- Enables preservation plans to be drafted more quickly and in a shorter period of time than conventional methods.
Aquatope®
Biotopes have problems such as water pollution and offensive odor due to algae proliferation. Aquatope® is a next-generation biotope that uses a proprietary functional charcoal to remove nitrate nitrogen, one of the factors that causes algae proliferation to achieve long-term conservation of water quality.
[Features of Aquatope®]
- Turning wastes into resources: Waste coffee grounds are modified and used as functional charcoal that can absorb nitrate nitrogen. Used functional charcoal is recycled as plant fertilizer.
- Water quality safety: As alghicides and the like are not used, there is no impact on the ecosystem.
- Improved biodiversity: Following construction of the Aquatope®, animals and insects that had not previously been seen appeared, and an improvement in biodiversity is expected.

Determination of Underwater Habitation Status of Rare Amphibians Using Environmental DNA Analysis Technology
A technology called environmental DNA analysis technology for analyzing the biological DNA (animal fragments, excrement etc.) in water and soil is used for an ongoing study of habitats of rare amphibians (salamanders) that inhabit conservation areas near a construction site. The use of this analysis technology makes it possible to determine the habitat status in water following spawning, which was difficult to accomplish by conventional visual inspection. This technology enables period. Long-term monitoring of habitat status during construcition period, making it possible to take more reliable protection measures.

Technologies for Purifying Contaminated Soil and Contaminated Groundwater
Since the 1990s, Taisei Corporation has been promoting the development of technologies for purifying soil and groundwater contamination. Taisei conducted 1,589 soil and groundwater surveys and 1,651 soil and groundwater purification projects since 1991. (As of March 2023)
Multi-barrier Method
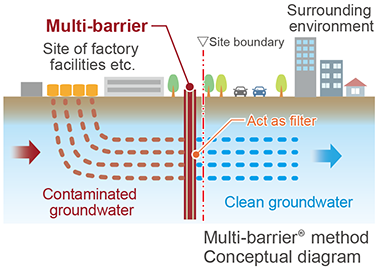
A permeable underground diaphragm wall is constructed on the downstream side of the groundwater flow to prevent the contaminants from flowing out from the site while purifying the contaminated groundwater using volatile organic compounds and heavy metals, etc. while preventing the contaminants from flowing out from the site.
- Enables maintenance-free in-situ groundwater treatment.
- Reliably prevents contaminated groundwater from spreading.
- Uses the permeable groundwater purification wall method that can deal with groundwater contaminated with various types of contaminants.
Flushing and bio-sparging method
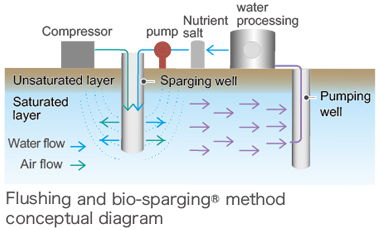
With this technology, a solution containing air and nutrient salts that activate the purification bacillus is provided to the groundwater, purifying the benzene and cyanogen compounds.
- The air and nutrient salts spread in the groundwater at the same time, resulting in even purification.
- Purification takes less time than the conventional microbial decomposition method.
- Purification of contamination ranging from highly concentrated to low-concentration contamination can be conducted without changing the method.
Technology for Preventing Groundwater Contamination by Nitrate Nitrogen
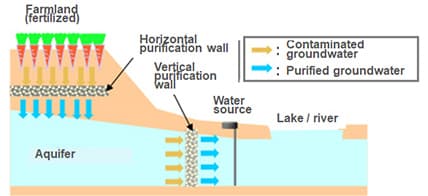
With this technology, a purification wall, which contains purification material (sustained-release organic matter) mixed in to release organic matter over a long period of time, is used to bring about a denitrification reaction in microorganisms in the groundwater flow channel that is contaminated with nitrate nitrogen. The nitrate nitrogen is converted into harmless gaseous nitrogen. Two types of purification walls have been developed: a vertical purification wall to protect water source regions and the like, and a horizontal purification wall placed beneath farmland that contains large quantities of fertilizer to reduce the load of nitrate nitrogen on aquifers.
- Purifies the nitrate nitrogen in groundwater for decades without obstructing use at the surface of the ground.
- Enables maintenance-free purification with no need for pumping up or other treatment.
- Purification technology uses the denitrification action of microorganisms, so safety is high and secondary contamination does not occur.
Cyclic Usage Technology for Slurry in Slurry Shield Tunnel Construction (Containing naturally occurring arsenic)
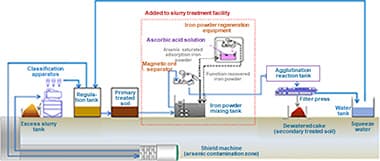
The slurry used in slurry shield tunnel construction is treated in a turbid water treatment plant, and the squeeze water that comes out of the dewatering process is reused. If arsenic or other contaminants are included, this process can remove the contaminants. The arsenic is also removed from the dewatered sludge (secondary treated soil), so it can be reused as well.
- Both water and soil can be resource-recycled.
- Technology for regenerating the iron powder to which the arsenic is attached enables the iron powder to be used repeatedly, reducing material costs and environmental load.
- The arsenic removal equipment is compact and can easily be installed in existing slurry treatment facilities.
New Toyosu Market Soil Contamination Remediation Project

This was a project to treat the contaminated soil and contaminated groundwater that had been contaminated by specified hazardous substances (benzene, cyanogen compounds, arsenic, lead, mercury, hexavalent chromium and cadmium) that had been produced by the operations of a city gas factory. The contaminated soil was transported to a temporary soil plant (separate work) and the treated soil was returned and used as backfill. The contaminated groundwater was purified by pumping-up and flushing using the flushing and bio-sparging method. The area subjected to soil contamination remediation measured approximately 130,000 m2.
Ⅲ. Conservation of water resources
Management of Construction Effluent
Taisei Corporation has been certified under ISO14001 and, as part of its Environmental Management System (EMS), exercises thorough management of construction effluent at all of its approximately 700 offices and workplaces both at home and abroad, using its own "Manual of Environmental Priorities for Branch Offices and Workplaces" and "Checklist of Environmental Laws and Regulations, etc. checklists."
In addition, various site patrols by general managers and branch officials as well as specialized environmental patrols (by environmental patrol personnel who have received training based on in-house standards) are conducted, in order to assess activities at each workplace and provide guidance for improvement.

- 1.During construction work planning, the Checklist of Environmental Laws and Regulations is used to confirm effluent destinations, effluent standards established in local ordinances, and relevant laws and ordinances.
- 2.Drainage methods and management plans are prepared, based on the characteristics of the surrounding environment and the construction site and effluent standards that are appropriate for the workplace.
- 3.If necessary, consultations with the government and the local community are held prior to the start of construction.
- 4.Workplaces manage water quality, such as the pH level of construction effluent, based on management plans. (The frequency of measurement varies depending on the workplace.)
- 5.Both regular and irregular environmental patrols are conducted and follow-up action is taken.
In construction projects, most of the activities at construction sites are conducted by subcontractors and suppliers, so coordination with such contractors is essential for environmental management at worksites, including the treatment and management of construction effluent. Taisei Corporation, together with some 7,000 primary subcontractors and suppliers, is conducting environmental management of its workplaces and striving to ensure that there are no environmental accidents. In the event of problem with the management of construction effluent by subcontractors and suppliers, or environmental accidents, reports are sent to Taisei Corporation without delay, and if the subcontractors and suppliers fail to fulfill its obligation, Taisei responds adequately, such as by suspending business with the offending subcontractors and suppliers.
Flood damage recovery
Emergency disaster measures for the levee breach on the Kinugawa River in the Tone River System
The concentrated heavy rainfall in the Kanto region in September 2015 resulted in a levee breach on September 10, extending for approximately 200m on a levee in the Kinugawa River. This caused damage that included many homes being washed away by the inundation flow in the area of the breach. Working 24 hours a day, Taisei Corporation conducted emergency repair work of the levee breach. A week after the breach, the placement of foot protection blocks and earth filling for the temporary embankment were completed. On September 24, two weeks after the breach, the emergency repair work that included the construction of a reinforcing double-wall cofferdam was successfully completed.
This emergency disaster recovery work was conducted based on a disaster relief agreement with the MLIT Kanto Regional Development Bureau.
Emergency work in the Aizome River System (recovery work following the Atami landslide disaster)
As emergency repair work on the Aizome River in the wake of the landslide that occurred on July 3, 2021 in the city of Atami, debris exclude works, construction roads and temporary dam works were constructed. To remove the rubble of the existing dam, helicopters were used for transport of earth and sand, and a wide access road on the right bank and construction roads were built to enable sediment transport by land as well. To prevent secondary disasters from occurring in downstream resident communities and the sectors where emergency recovery work was underway, net roll sandbags and temporary block dams were constructed in the FY 2021 work. The FY 2022 work will focus on construction of the new permanent dam.
T-Flood® Analyzer Flood Risk Assessment System
This technology simulates the building interior inundation status in the event that the area around the building is flooded and inundated. The results of analysis, such as the inundation path to each room in the building, the inundation quantity and the inundation time are visualized at an arbitrary location, thus enables to grasp the inflow route to each room in the building and the depth of flooding at a glance.
In addition, the shortest evacuation route from each room to the ground level exit and the time required in the event of flooding can also be calculated.
And the results of analysis can be displayed in three dimensions from an arbitrary perspective, making it easy to share inundation status and inundation risk data among participants and enabling it to be used effectively as a consensus-building tool as well.
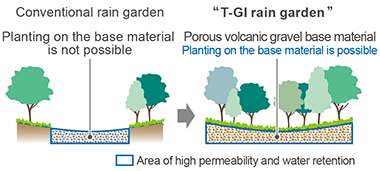
"T-GI® Rain Garden" Outdoor Facility Creation Technology with Advanced Rainwater Permeability and Storage Functions
TAISEI developed the "T-GI® Rain Garden" outdoor facility creation technology which uses a new planting base material that combines rainwater permeability with storage performance, and confirmed its effectiveness through demonstration tests.
T-GI® Rain Garden has the following features.
- 1.Base material offers excellent rainwater permeability and storage functions.
A porous volcanic gravel with high water retention is used, and volcanic gravel of different grain sizes are blended to create voids in the soil, and thus realized a base material with excellent rainwater permeability and storage capabilities. - 2.Can be planted directly on the base material, expanding the planting area.
Ordinary base material use gravel and the like as the base material which are good in permeability but have poor water retention, and thus, not suitable for planting trees. The newly developed base material not only allows rainwater to permeate, but also stores rainwater in the material, thus enables planting directly on the base material and makes it possible to expand the range of applications for rain garden. - 3.Possible to reduce or delay the peak of rainwater runoff from the site during rain.
The base material is effective in reducing or delaying the peak of rain runoff from the site during rainfall (in actual measurements, the peak of rainfall runoff was reduced approximately 85%, and in indoor tests the time of peak runoff was delayed by 35 to 60 minutes), so it can contribute to prevent urban area floodings. - 4.Various types of plants can be cultivated.
As the base material can stores rainwater temporarily, it has been confirmed to be capable of nurturing a wide variety of plants, for environments ranging from humid to somewhat arid environments. As a result, various types of greenery can be created.
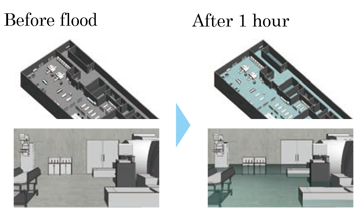
Business Continuity Plan (BCP)
To continue business operations even in the event that the head or branch offices and construction workplaces sustain flood damage or other types of damage, a Business Continuity Plan (BCP) has been formulated, and trainings are conducted each year. The content of the BCP is revised as needed to ensure that it reflects disaster damage that has actually occurred and the social situation. Each year, approximately JPY 100 million is disbursed for equipment and system maintenance and the purchase of stockpiles and so on.
